A Comprehensive Exploration of Quality Control in the Jewelry Industry: Ensuring Excellence in Every Piece
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Quality Control in the Jewelry Industry: Ensuring Excellence in Every Piece
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Quality Control in the Jewelry Industry: Ensuring Excellence in Every Piece. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Quality Control in the Jewelry Industry: Ensuring Excellence in Every Piece

The jewelry industry, known for its exquisite craftsmanship and enduring beauty, relies heavily on rigorous quality control (QC) processes to ensure the delivery of exceptional products. This article delves into the crucial role of QC in jewelry manufacturing, examining its multifaceted aspects, benefits, and the importance of implementing robust systems.
Understanding the Significance of Quality Control in Jewelry
Quality control in jewelry encompasses a systematic approach to verifying and maintaining the highest standards throughout the entire production process. From raw material sourcing to the final polish, each stage undergoes meticulous inspection to ensure conformity with predetermined criteria.
Benefits of Implementing Robust Quality Control Systems
- Enhanced Product Quality: Stringent QC practices lead to a consistent level of excellence in every piece of jewelry produced. This translates to durable, visually appealing, and functionally sound products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Minimized Defects and Returns: Thorough inspections and testing at various stages identify and eliminate potential defects early on, reducing the likelihood of flawed products reaching consumers. This minimizes customer dissatisfaction and costly product returns.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: A commitment to quality control fosters a strong brand reputation, building customer trust and loyalty. Consumers associate high-quality jewelry with brands that prioritize meticulous craftsmanship and consistent excellence.
- Cost Optimization: While implementing robust QC systems may seem like an added expense, it ultimately optimizes costs by preventing costly rework, product recalls, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: The jewelry industry operates under strict regulations and ethical guidelines. Quality control measures ensure compliance with these standards, safeguarding both the brand and its customers.
Key Stages of Quality Control in Jewelry Manufacturing
1. Raw Material Inspection:
- Source Verification: Sourcing materials from reputable suppliers is paramount. QC protocols involve verifying the origin, quality, and certifications of precious metals, gemstones, and other materials.
- Metal Purity and Composition: Metal purity is crucial for the durability and value of jewelry. QC tests ensure that the metal composition meets established standards and specifications.
- Gemstone Quality Assessment: Gemstone quality is evaluated based on factors such as clarity, color, cut, and carat weight. Experts use specialized tools and techniques to grade gemstones according to established criteria.
2. Production Process Control:
- Casting and Molding: QC checks the casting process for accuracy, ensuring that the mold replicates the design precisely. Surface quality and dimensional accuracy are also scrutinized.
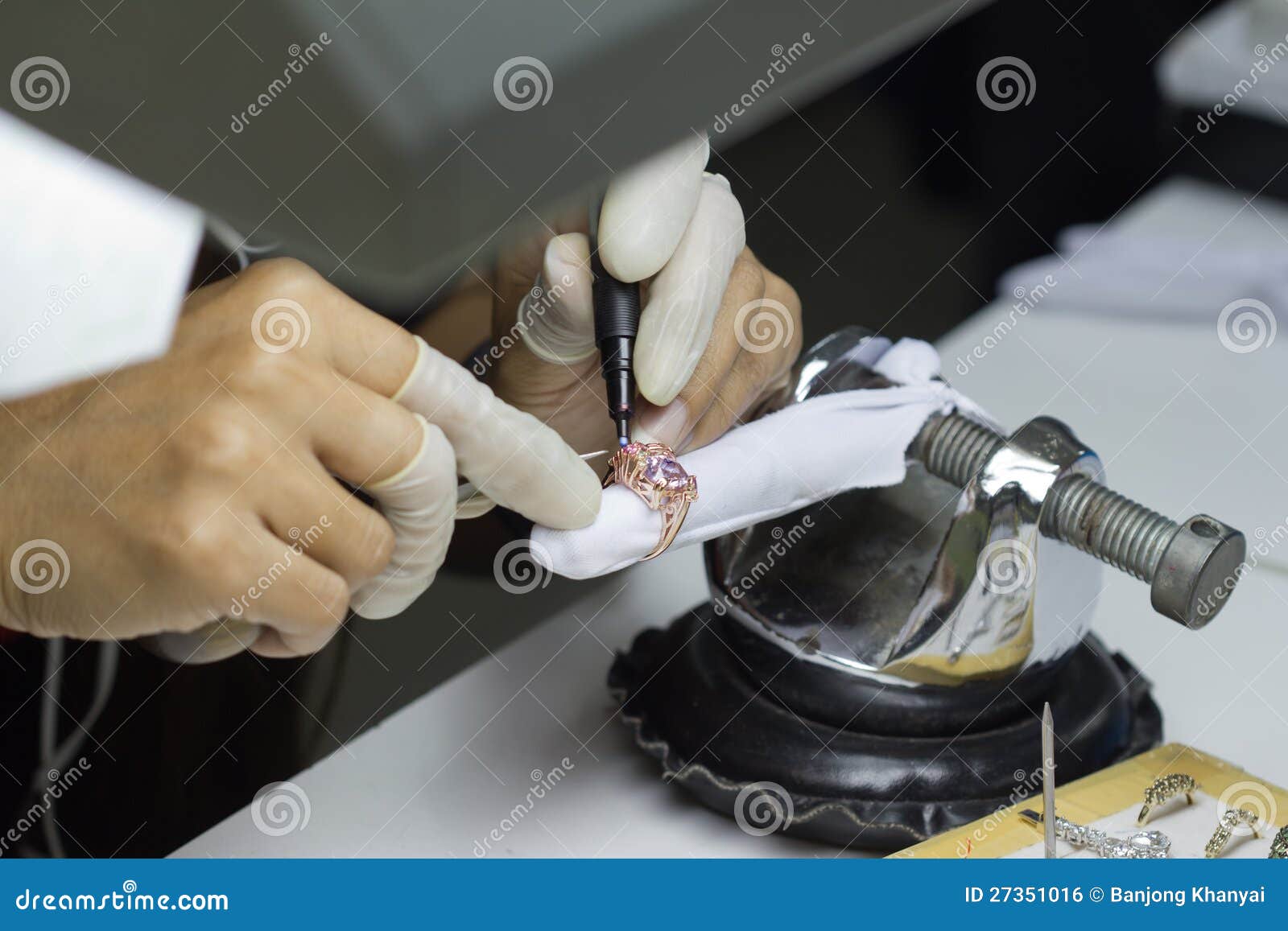
- Setting and Mounting: The setting of gemstones and the mounting of other components are carefully inspected for secure placement, stability, and proper alignment.
- Polishing and Finishing: QC ensures that the final polishing and finishing processes achieve the desired shine, smoothness, and overall aesthetic appeal.
3. Final Inspection and Quality Assurance:
- Dimensional Accuracy: All pieces are meticulously measured to ensure adherence to the original design specifications. Any deviations are identified and addressed.
- Functionality and Wearability: The functionality of clasps, hinges, and other mechanisms is tested, and the overall wearability of the piece is assessed.
- Appearance and Aesthetics: The final inspection focuses on the overall appearance of the jewelry, ensuring it meets the highest aesthetic standards.
4. Packaging and Labeling:
- Packaging Integrity: The packaging used to protect and present the jewelry is inspected for quality and proper labeling.
- Product Information: Labels must accurately reflect the material composition, gemstone details, and other relevant product information.
5. Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement:
- Data Analysis: Regular analysis of QC data helps identify recurring issues and areas for improvement.
- Process Optimization: Data-driven insights inform continuous improvement strategies, optimizing production processes and minimizing defects.
- Employee Training: Ongoing training for QC personnel ensures they remain up-to-date with the latest industry standards and techniques.
Implementing Effective Quality Control Measures
- Clearly Defined Standards: Establish clear, measurable quality standards for all aspects of the production process.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Maintain detailed records of QC procedures, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken.
- Qualified Personnel: Invest in skilled and knowledgeable QC personnel who are trained in industry-specific techniques and standards.
- Modern Equipment and Technology: Utilize advanced inspection tools and technologies to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct periodic audits and reviews to assess the effectiveness of QC systems and identify areas for improvement.
The Importance of Transparency and Communication
- Open Communication: Establish open communication channels between all stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
- Traceability: Maintain a transparent chain of custody for all materials and products, enabling easy tracking and accountability.
- Customer Feedback: Actively solicit and address customer feedback, using it to improve QC processes and enhance customer satisfaction.
FAQs on Quality Control in Jewelry
Q: What are the common types of defects found in jewelry?
A: Common defects include:
- Metal defects: Scratches, dents, misaligned components, uneven surfaces, and improper metal composition.
- Gemstone defects: Imperfect clarity, color inconsistencies, loose settings, and chipped or broken gemstones.
- Manufacturing defects: Incorrect sizing, faulty clasps or closures, and uneven finishing.
Q: How can I identify if a piece of jewelry has been subjected to proper quality control?
A: Look for:
- Brand Reputation: Choose jewelry from reputable brands known for their quality and craftsmanship.
- Hallmarks and Certifications: Check for hallmarks indicating the metal purity and certifications for gemstones.
- Detailed Product Information: Look for detailed product descriptions and specifications, including material composition and gemstone details.
- Customer Reviews: Read customer reviews to gauge the overall quality and satisfaction levels.
Q: What are the consequences of inadequate quality control in jewelry?
A: Inadequate QC can lead to:
- Damaged Brand Reputation: Customer dissatisfaction and product returns can negatively impact a brand’s reputation and erode consumer trust.
- Financial Losses: Rework, product recalls, and customer refunds can incur significant financial losses.
- Legal Issues: Defective jewelry can pose safety risks and lead to legal liability.
Tips for Jewelry Manufacturers and Retailers:
- Invest in comprehensive QC systems: Prioritize quality control by allocating sufficient resources and personnel.
- Implement continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate QC processes and implement data-driven improvements.
- Empower QC personnel: Provide adequate training and support to QC personnel to ensure they have the knowledge and authority to enforce quality standards.
- Collaborate with suppliers: Establish strong partnerships with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality and adhere to industry standards.
- Prioritize customer satisfaction: Actively solicit and respond to customer feedback, using it to improve QC processes and build trust.
Conclusion
Quality control is a critical aspect of the jewelry industry, playing a vital role in ensuring the production of high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing products. By implementing robust QC systems, jewelry manufacturers and retailers can build a strong brand reputation, minimize defects, optimize costs, and ultimately deliver an exceptional customer experience. A commitment to quality control is not merely a business practice but an essential element in upholding the integrity and enduring value of the jewelry industry.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Quality Control in the Jewelry Industry: Ensuring Excellence in Every Piece. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!