Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training
Related Articles: Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training
- 3.1 The Importance of Formal Education
- 3.2 Types of Schools and Programs
- 3.3 Essential Skills and Qualifications
- 3.4 Finding the Right Program
- 3.5 FAQs about Schools to Become a Jeweler
- 3.6 Tips for Success in Jewelry Making
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training
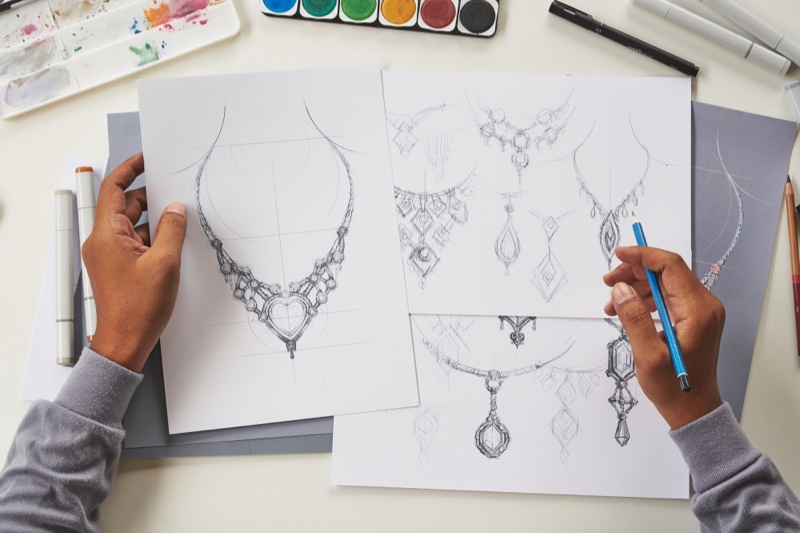

The allure of jewelry is undeniable. From the intricate designs to the precious materials, the art of jewelry making has captivated people for centuries. If you are drawn to this world of craftsmanship and creativity, a career as a jeweler can be both fulfilling and rewarding. However, embarking on this path requires dedicated training and education. This comprehensive guide will explore the various avenues to becoming a skilled jeweler, outlining the types of schools, programs, and essential skills needed to succeed in this exciting field.
The Importance of Formal Education
While some may assume that artistic talent is the sole requirement for becoming a jeweler, formal education plays a crucial role in developing the necessary technical skills and knowledge. A well-structured program provides a solid foundation in:
- Design and Aesthetics: Understanding the principles of design, color theory, and proportion is essential for creating visually appealing and harmonious jewelry pieces.
- Metalworking Techniques: Jewelers must master various metalworking techniques, including soldering, casting, forging, and finishing.
- Gemology and Materials: Identifying different gemstones, understanding their properties, and selecting the right materials for specific designs are crucial aspects of jewelry making.
- Business and Marketing: For those seeking to establish their own jewelry businesses, courses in business management, marketing, and finance are invaluable.
Types of Schools and Programs
Aspiring jewelers have several educational options to choose from:
1. Trade Schools and Vocational Programs:
These programs offer hands-on training in jewelry making techniques, often focusing on specific crafts like bench jewelry, metal casting, or gem setting. They typically provide a practical, skill-oriented curriculum, preparing students for immediate entry into the jewelry industry.
2. Community Colleges:
Many community colleges offer associate degrees in jewelry design or related fields. These programs combine theoretical knowledge with practical training, often including courses in design, metalworking, gemology, and business.
3. Art Schools and Universities:
Art schools and universities offer bachelor’s degrees in jewelry design, fine arts, or related fields. These programs often emphasize artistic expression, design theory, and conceptual thinking, providing a more in-depth understanding of the art and craft of jewelry making.
4. Apprenticeship Programs:
Apprenticeships offer a combination of on-the-job training and formal education. Under the guidance of experienced jewelers, apprentices gain hands-on experience while learning the nuances of the trade. These programs can be highly competitive, requiring a strong work ethic and commitment.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Beyond formal education, aspiring jewelers must cultivate a set of essential skills:
- Fine Motor Skills: Jewelry making requires precision and dexterity to handle delicate tools and materials.
- Creativity and Design Sense: Jewelers must translate their ideas into visually appealing and functional designs.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Challenges arise in the jewelry making process, requiring creative problem-solving and adaptability.
- Attention to Detail: Every aspect of jewelry making, from metalwork to gem setting, demands meticulous attention to detail.
- Patience and Perseverance: Jewelry making can be a time-consuming and demanding craft, requiring patience and perseverance to achieve desired results.
Finding the Right Program
Choosing the right school or program is crucial for success. Here are some factors to consider:
- Program Curriculum: Review the curriculum to ensure it aligns with your career goals and interests.
- Faculty Expertise: Research the qualifications and experience of the instructors.
- Facilities and Equipment: Assess the quality and availability of the workshops, tools, and materials.
- Industry Connections: Look for programs that offer opportunities for internships, networking, and industry collaborations.
- Accreditation: Ensure the program is accredited by a recognized body, signifying quality and standards.
FAQs about Schools to Become a Jeweler
1. What is the typical length of a jewelry making program?
Program lengths vary depending on the level of education. Trade schools and vocational programs typically range from a few months to a year. Community college associate degrees usually take two years, while university programs can take four years for a bachelor’s degree.
2. What are the typical costs associated with jewelry making programs?
Tuition and fees vary widely depending on the institution and program. Trade schools and community colleges often have lower costs compared to art schools and universities.
3. What are the job prospects for jewelers?
The job market for jewelers can be competitive. However, demand exists for skilled and creative jewelers in various sectors, including:
- Retail Jewelry Stores: Sales and repair of jewelry.
- Jewelry Manufacturing: Production of jewelry for wholesale and retail markets.
- Custom Jewelry Design: Creating bespoke pieces for individual clients.
- Art and Design: Jewelry as an art form, showcased in galleries and exhibitions.
4. What are the potential career paths for jewelers?
With experience and expertise, jewelers can pursue various career paths:
- Bench Jeweler: Specializing in specific jewelry making techniques like setting, casting, or engraving.
- Designer Jeweler: Creating original jewelry designs and collaborating with manufacturers.
- Jewelry Appraiser: Assessing the value and authenticity of jewelry.
- Jewelry Educator: Teaching jewelry making skills in schools, workshops, or private studios.
5. Are there any certifications or licenses required to become a jeweler?
While specific certifications or licenses are not mandatory in all jurisdictions, certain certifications can enhance credibility and marketability. These include:
- Gemological Institute of America (GIA) Graduate Gemologist (GG) Certification: Demonstrates expertise in gemology and gemstone identification.
- American Gem Society (AGS) Certified Gemologist Appraiser (CGA) Certification: Qualifies individuals to appraise jewelry and gemstones.
- Certified Bench Jeweler (CBJ) Certification: Recognizes proficiency in bench jewelry making techniques.
Tips for Success in Jewelry Making
- Develop Strong Technical Skills: Master the fundamentals of metalworking, gem setting, and design.
- Stay Updated on Trends: Keep abreast of current design trends and innovations in jewelry making.
- Network with Other Jewelers: Build relationships with other professionals in the industry for collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Showcase Your Work: Create a portfolio to showcase your skills and designs to potential clients and employers.
- Consider Specializing: Focus on a specific niche or area of expertise to stand out in a competitive market.
Conclusion
The path to becoming a successful jeweler is paved with dedication, creativity, and continuous learning. By pursuing formal education, developing essential skills, and embracing the challenges of the craft, aspiring jewelers can forge fulfilling careers in this captivating industry. Whether creating exquisite pieces for discerning clients or contributing to the world of art and design, the journey of a jeweler is one of artistic expression, technical mastery, and the enduring allure of precious materials.
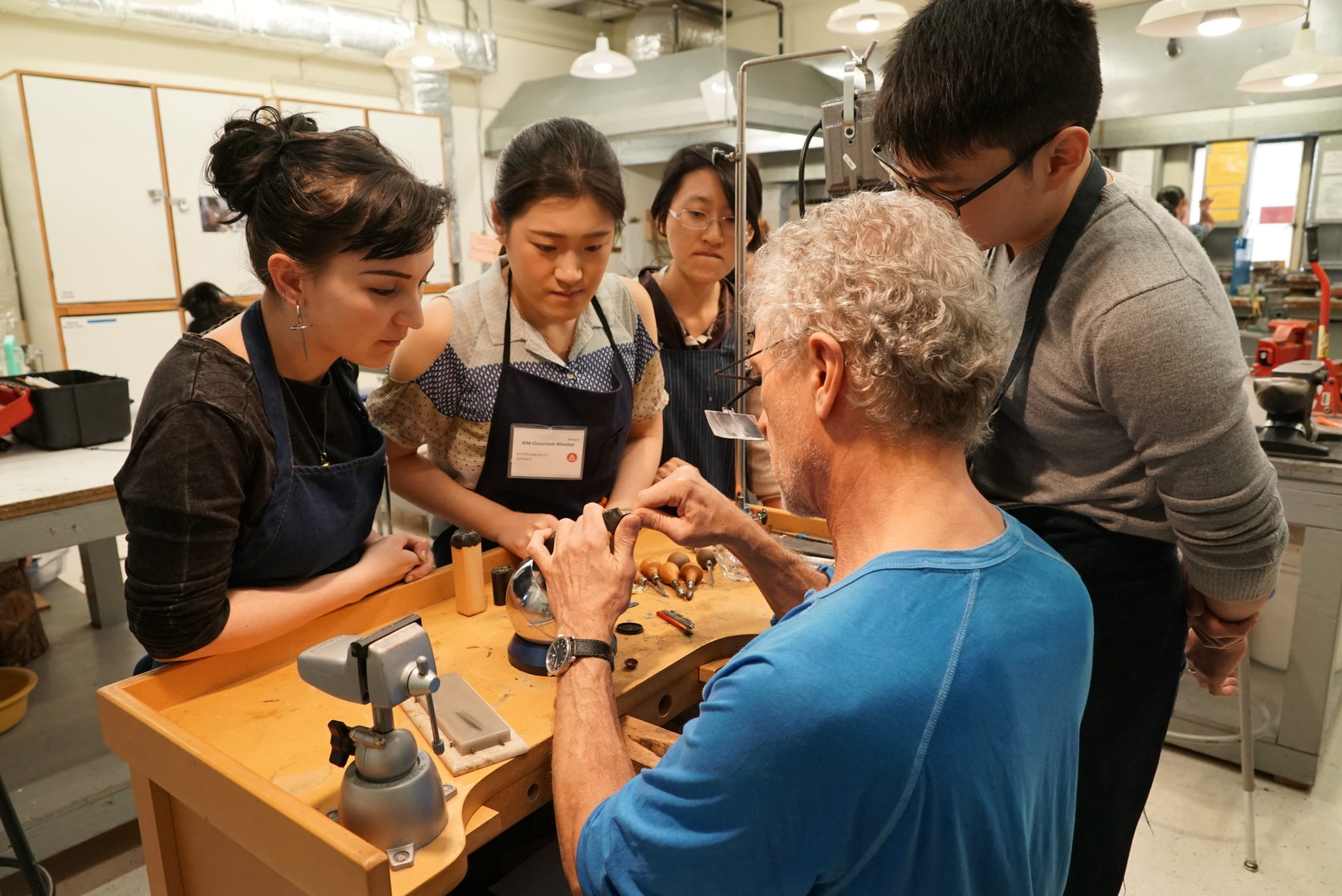
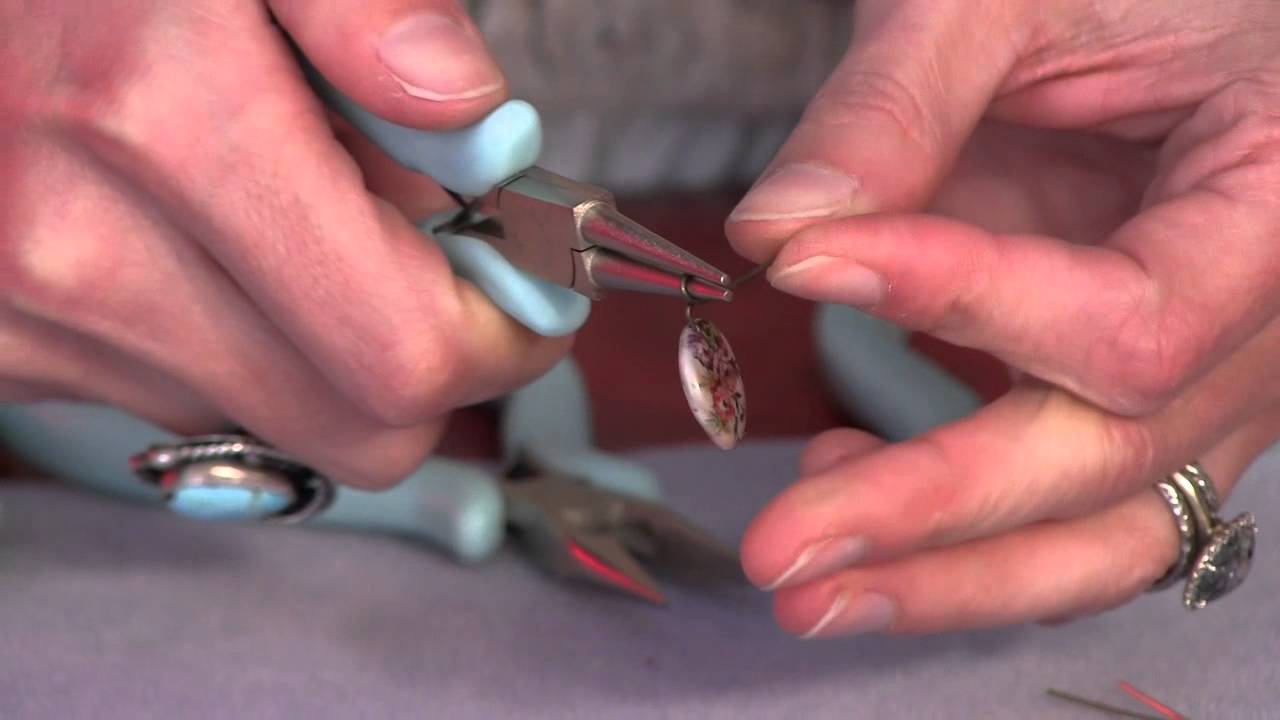
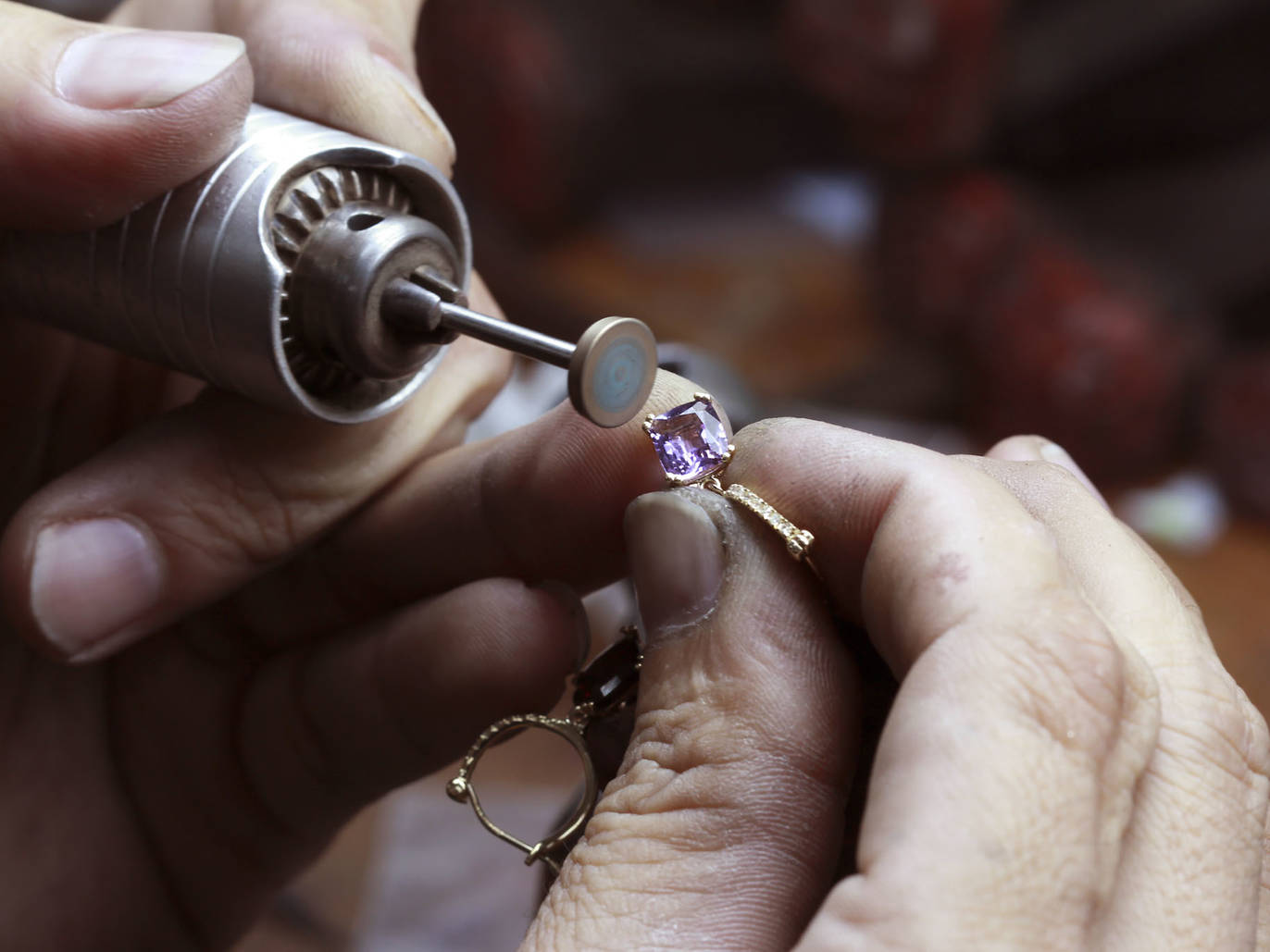







/200419786-011-56b06c585f9b58b7d0232f85.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Crafting a Career in Jewelry: A Guide to Schools and Training. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!