Soldering Jewellery Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Joining Metal
Related Articles: Soldering Jewellery Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Joining Metal
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Soldering Jewellery Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Joining Metal. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Soldering Jewellery Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Joining Metal

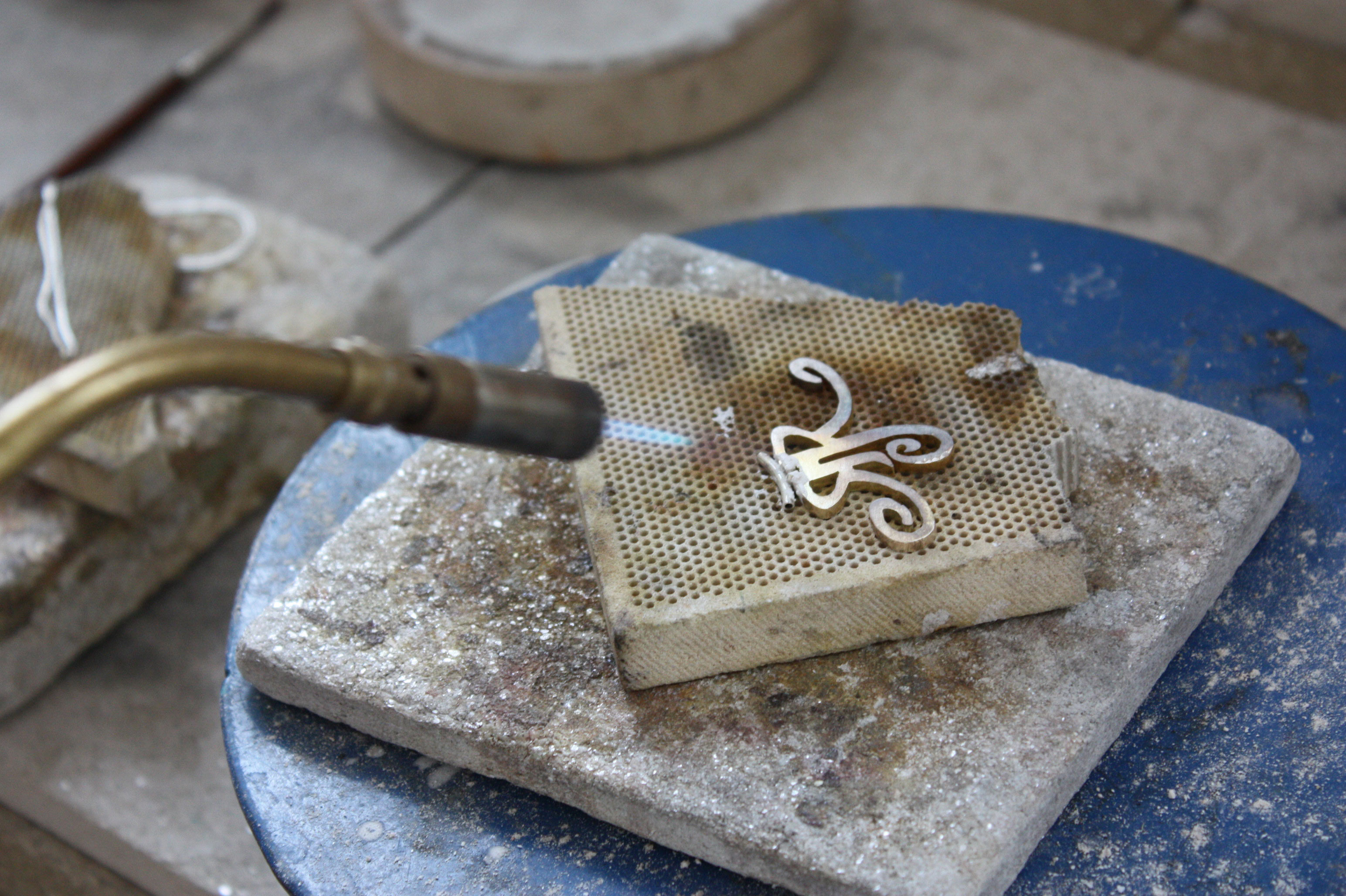
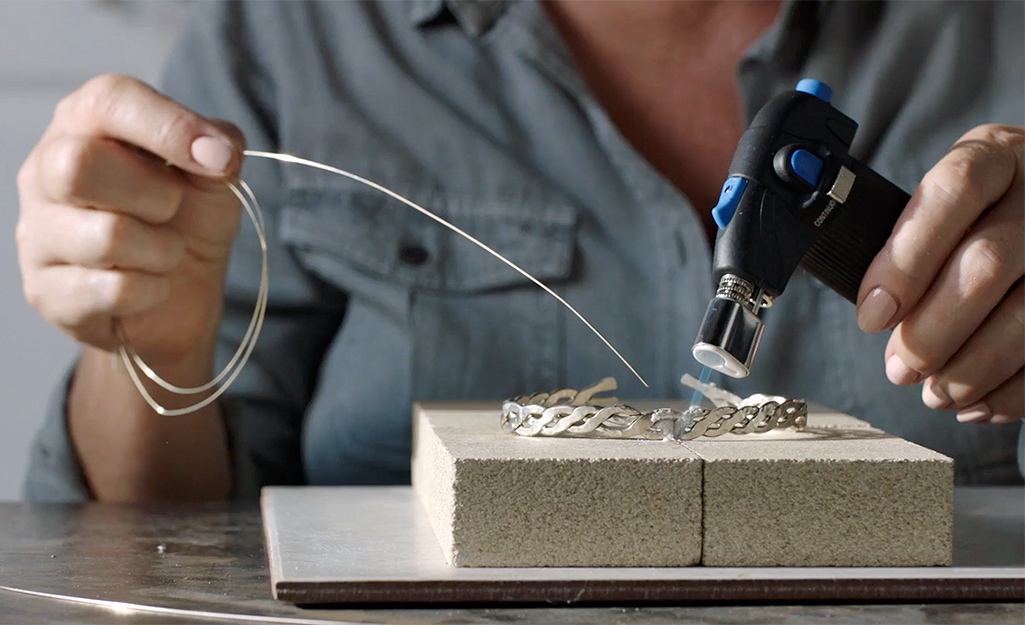
Soldering is a fundamental technique in jewellery making, allowing artisans to permanently join different metal pieces together. It involves using a filler metal, known as solder, which melts at a lower temperature than the base metal, creating a strong and durable bond. This process is essential for crafting intricate designs, assembling components, and creating robust structures.
Understanding the Basics of Soldering
Soldering relies on the principle of capillary action. When solder is heated to its melting point, it flows into the gap between two metal pieces, creating a strong metallurgical bond. This bond is achieved through the process of alloying, where the solder atoms intermix with the base metal atoms, forming a cohesive structure.
Types of Solder and Their Applications
Solder is categorized by its melting point and composition, each suitable for different metals and applications:
- Soft Solder: This type melts at relatively low temperatures (typically below 450°F), making it ideal for joining metals with low melting points, such as silver, copper, and brass. It is often used for delicate work and repairs.
- Hard Solder: With a higher melting point (above 450°F), hard solder is stronger and more durable, suitable for joining metals with higher melting points, such as gold, platinum, and steel. It is commonly used in structural applications.
- Silver Solder: This type is a popular choice for silver jewellery, offering a wide range of melting points and compositions to suit different applications. It is known for its excellent flow characteristics and strength.
- Gold Solder: Similar to silver solder, gold solder is available in various melting points and compositions. It is specifically designed for joining gold and other precious metals, providing a strong and aesthetically pleasing bond.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Soldering
Soldering requires specific tools and equipment to ensure a safe and successful process:
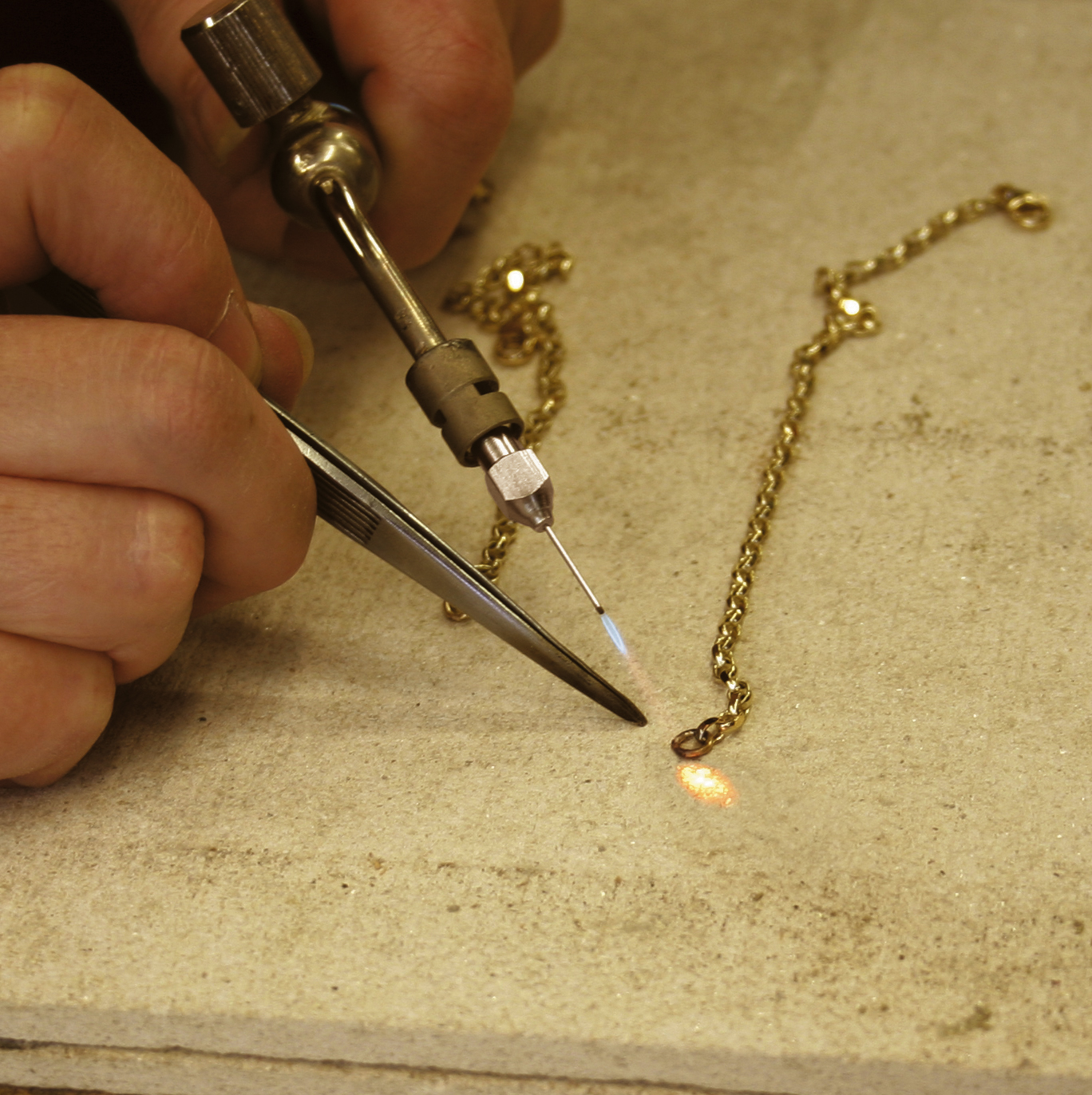
- Torch: A torch is used to heat the metal pieces and the solder to their melting points. There are various types of torches available, including propane torches, butane torches, and oxy-acetylene torches, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Soldering Iron: An alternative to a torch, a soldering iron is a handheld tool with a heated tip that melts the solder. It is particularly useful for smaller projects and delicate work.
- Flux: Flux is a chemical paste or liquid that is applied to the metal surfaces before soldering. It removes oxides and other impurities, promoting better solder flow and a stronger bond.
- Soldering Board: A soldering board provides a heat-resistant surface for holding the metal pieces during the soldering process. It can be made of firebrick, ceramic, or other heat-resistant materials.
- Safety Glasses: Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris and intense heat.
- Gloves: Heat-resistant gloves are essential to protect your hands from burns.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes from the solder and flux.
Soldering Techniques: A Step-by-Step Guide
The specific steps involved in soldering vary depending on the project, the type of solder, and the preferred technique. However, the following general steps provide a comprehensive overview:
- Preparation: Clean the metal surfaces thoroughly with a suitable cleaning agent to remove any dirt, grease, or oxides. This ensures good adhesion and prevents weak bonds.
- Fluxing: Apply flux to the metal surfaces that will be joined. The flux will create a protective layer and aid in the soldering process.
- Heating: Use a torch or soldering iron to heat the metal pieces to the melting point of the solder. It is important to heat the entire area where the solder will be applied, ensuring even distribution of heat.
- Soldering: Carefully apply the solder to the heated metal pieces, allowing it to flow into the gap between them. Use a small amount of solder and ensure it completely fills the gap.
- Cooling: Allow the soldered pieces to cool slowly and naturally. Avoid sudden temperature changes, as this can cause stress and weaken the bond.
Important Considerations for Successful Soldering
- Temperature Control: Maintaining the correct temperature is crucial for successful soldering. Too low a temperature will prevent the solder from melting properly, while too high a temperature can cause damage to the metal pieces.
- Proper Flux Application: Applying the correct amount of flux and ensuring it covers the entire area to be soldered is essential for a strong and durable bond.
- Solder Flow: The solder should flow smoothly and completely fill the gap between the metal pieces. If the solder does not flow properly, it may indicate an issue with the temperature, flux, or metal preparation.
- Safety Precautions: Always wear safety glasses and heat-resistant gloves when soldering. Ensure adequate ventilation and work in a well-lit area.
Advanced Soldering Techniques
Beyond the basic soldering techniques, there are several advanced methods used by experienced jewellers:
- Torch Soldering: This technique utilizes a torch to heat the metal pieces and solder, allowing for greater control over the heat application. It is suitable for larger projects and structural work.
- Micro-Soldering: This technique involves using a specialized soldering iron with a very fine tip, ideal for delicate work, such as setting stones or repairing intricate pieces.
- Brazing: Similar to soldering, brazing uses a filler metal with a higher melting point than the base metal, creating a stronger bond. It is often used for joining thicker pieces of metal or for applications requiring high strength.
- Laser Soldering: This advanced technique uses a laser beam to melt the solder, offering precise control and minimal heat distortion. It is particularly useful for delicate and complex work.
FAQs about Soldering Jewellery Techniques
Q: What is the best type of solder for jewellery?
A: The best type of solder depends on the specific metal and application. For silver jewellery, silver solder is commonly used, while gold solder is preferred for gold jewellery. The melting point and composition of the solder should be chosen based on the metal’s properties and the desired strength of the bond.
Q: How do I know if I’m using the right solder?
A: The solder should melt at a lower temperature than the base metal but high enough to create a strong bond. Refer to solder charts or consult with an experienced jeweller to determine the appropriate solder for your project.
Q: How do I prevent solder from flowing where I don’t want it?
A: Use a soldering block or heat sink to direct the heat to the desired area. You can also apply a heat-resistant material, such as charcoal or ceramic, to areas you don’t want to solder.
Q: How do I remove excess solder?
A: Once the solder has cooled, you can remove any excess solder using a file, sandpaper, or a small chisel.
Q: How do I clean soldered pieces?
A: After soldering, clean the pieces with a suitable cleaning agent to remove any flux residue or oxides. This will restore the metal’s shine and prevent tarnishing.
Tips for Successful Soldering
- Practice: Soldering is a skill that requires practice and patience. Start with simple projects and gradually work your way up to more complex designs.
- Use the Right Tools: Invest in high-quality tools and equipment, as they will make the soldering process easier and more successful.
- Be Patient: Soldering requires careful attention to detail and precise temperature control. Do not rush the process, and allow the solder to cool slowly and naturally.
- Experiment: Try different soldering techniques and approaches to find what works best for you.
- Seek Guidance: If you are new to soldering, seek guidance from an experienced jeweller or take a workshop to learn the proper techniques.
Conclusion
Soldering is a fundamental technique in jewellery making, enabling artisans to join metal pieces together with strength and durability. By understanding the different types of solder, the essential tools and techniques, and the important considerations for a successful process, jewellers can create intricate designs, assemble components, and craft beautiful and lasting jewellery pieces. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced jeweller, mastering soldering techniques is essential for realizing your creative vision and producing high-quality jewellery.

/153083523-F-56a03f4d3df78cafdaa0aa21.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Soldering Jewellery Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Joining Metal. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!